- Tech support scams are an industry-wide issue where scammers trick you into paying for unnecessary technical support services. You can help protect yourself from scammers by verifying that the contact is a Microsoft Agent or Microsoft Employee and that the phone number is an official Microsoft global customer service number.
- The successful installation is logged in the Application Event Log with a message ID of 11707 (1707 + 10,000). For information about how to enable verbose logging on a user's computer when troubleshooting deployment, see Windows Installer Best Practices.
- Event Id 1112 Software Installation Tool
- Event Id 1112 Software Installation Software
- Event Id 1112 Software Installation Manual
Update the GPO by running the command gpupdate/force and restart computer to check install the software on machine startup. Are you looking for the MSI package builder software? All the packages created with Advanced Installer are GPO/Intune/ConfigMgr ready for deployment etc. Create MSI in minutes.
Symptom: When browsing through the event viewer logs on your Windows Update Services server, you notice the following Event IDs with a Level of Errorin the following order: 12052, 12042, 12022, 12032, 12012, 12002, 13042.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Event ID: 12052
Task Category: 9
Level: Error
Description: The DSS Authentication Web Service is not working.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Date: 10/3/2013 4:53:26 AM
Event ID: 12042
Task Category: 9
Level: Error
Description: The SimpleAuth Web Service is not working.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Date: 10/3/2013 4:53:26 AM
Event ID: 12022
Task Category: 9
Level: Error
Description: The Client Web Service is not working.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Date: 10/3/2013 4:53:26 AM
Event ID: 12032
Task Category: 9
Level: Error
Description: The Server Synchronization Web Service is not working.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Date: 10/3/2013 4:53:26 AM
Event ID: 12012
Task Category: 9
Level: Error
Description: The API Remoting Web Service is not working.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Date: 10/3/2013 4:53:26 AM
Event ID: 12002
Task Category: 9
Level: Error
Description: The Reporting Web Service is not working.
Log Name: Application
Source: Windows Server Update Services
Date: 10/3/2013 4:53:26 AM
Event ID: 13042
Task Category: 6
Level: Error
Description: Self-update is not working.
Additionally, you can recreate these events by running the following command: wsusutil.exe checkhealth
Solution: Reconfigure the WSUS server via the wsusutil.exe command.
- Login to the WSUS server
- Open up a command prompt with Administrative rights
- Navigate to the Update ServicesTools directory.
- By default you can find it on your C drive by executing the following command
- cd “c:Program FilesUpdate ServicesTools”
- cd “c:Program FilesUpdate ServicesTools”
- By default you can find it on your C drive by executing the following command
- Execute one of the following commands
- If updates are configured for port 80 execute this command
- wsusutil.exe usecustomwebsite false
- If updates are configured for port 8530 execute this command
- wsusutil.exe usecustomwebsite true
- If updates are configured for port 80 execute this command
- Execute the following command to verify the WSUS service is running correctly
- wsusutil.exe checkhealth
- wsusutil.exe checkhealth
- You should see Event ID 10000 in event viewer confirming all is well
This article provides the methods to solve the Netlogon event ID 5719 or Group Policy event 1129 that is logged when you start a domain member.
Original product version: Windows 10 - all editions, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 938449
Symptoms
Important
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, back up the registry for restoration in case problems occur.
Consider this scenario:
- You have a computer that's running Windows 10 or Windows Server 2012 R2.
- The computer is joined to a domain.
- One of these conditions is true:
- The computer has a Gigabit network adapter installed.
- You secure the network access by using Network Access Protection (NAP), network authentication (by using 802.1x), or another method.
In this scenario, the following event is logged in the System log when you start the computer in every version of Windows up to and including Windows 8.1. In Windows 10 and newer versions, event 5719 is no longer logged in this situation. Instead, the following lines are recorded in Netlogon.log:
[CRITICAL] [960] CONTOSO: NlSessionSetup: Session setup: cannot pick trusted DC
[SESSION] [960] No IP addresses present, skipping No DC event log
After this occurs, the computer is assigned an IP address:
[SESSION] [960] V6 Winsock Addrs: fe80::5faf:632a:f22c:644a%2 (1) V6WinsockPnpAddresses List used to be empty.
[SESSION] [960] Winsock Addrs: 10.1.1.80 (1) List used to be empty.
On Windows 10 and later versions, you'll see only events by components, depending on the Domain Controller connectivity (such as Group Policy). The following is recorded in the group policy debug log:
CGPApplicationService::MachinePolicyStartedWaitingOnNetwork.
CGPMachineStartupConnectivity::CalculateWaitTimeoutFromHistory: Average is 388.CGPMachineStartupConnectivity::CalculateWaitTimeoutFromHistory: Current is -1.CGPMachineStartupConnectivity::CalculateWaitTimeoutFromHistory: Taking min of 776 and 30000.
Waiting for SamSs with timeout 776
NlaQueryNetSignatures returned 1 networks
NSI Information (Network GUID) : {395DB3C8-CE45-11E5-9739-806E6F6E6963}
NSI Information (CompartmentId) : 1
NSI Information (SiteId) : 134217728
NSI Information (Network Name) :
NlaGetIntranetCapability failed with 0x15
There is no domain compartment
ProcessGPOs(Machine): MyGetUserName failed with 1355.
Opened query for NLA successfully
NlaGetIntranetCapability returned Not Ready error. Consider it as NOT intranet capable.
GPSVC(530.ae0) 13:32:28:728 There is no connectivity
GPSVC(530.8e0) 13:32:28:728 ApplyGroupPolicy: Getting ready to create background thread GPOThread.
The first section shows the calculation for the time-out to use to bring up the network. This can be based on previous fast startups.
The second section shows that NLA fails to report a working network within the wait interval that is allowed, and group policy startup processing fails. The third section shows that the Group Policy engine starts a background procedure, and then waits for one minute after a network becomes available.
Cause
This issue may occur for any of these reasons:
- The Netlogon service starts before the network is ready. The network stack and adapter initialization often start at about the same time. Some network adapters and switches have link arbitration and MAC address uniqueness checks that take longer to complete than the wait time that is set for Netlogon to detect network connectivity.
- Solutions that verify the health of the new network member delay the network connection and your ability to access domain controllers. If you have an automatic Direct Access channel connection enabled, this may also require more time to do than Netlogon allows.
- The 802.1X authentication process delays connections to the domain controllers.
- The client experiences a delay to retrieve an IP address from the DHCP server. This delays the display of the network interface.
Group Policy in Windows Vista and later versions is written to negotiate the network status that has Network Location Awareness (NLA) enabled, and it waits for a network that has DC connectivity. However, Group Policy may start prematurely because of a policy application. This is especially true when the delay in finding a network alternates between startups.
Warning
Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall the operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your own risk.
Resolution 1
To resolve this issue, install the most current driver for the Gigabit network adapter. Or, enable the PortFast option on the network switches.
Resolution 2
To resolve this issue, use the registry to change the related settings that affect DC connectivity. To do this, use the following methods.
Method 1
Adjust the firewall settings or IPSEC policies that are changed to allow DC connectivity. These changes are made when the client receives an IP address but requires more time to access a domain controller (for example, after a successful verification through Cisco NAC or Microsoft NPS Services).
Method 2
Configure the Netlogon registry setting to a value that is safely beyond the time that is required allow DC connectivity.
Note
This is only effective if the machine already has an IP address. This applies to scenarios where a NAP solution puts the machine into a quarantine network. Use the following settings as guidelines.
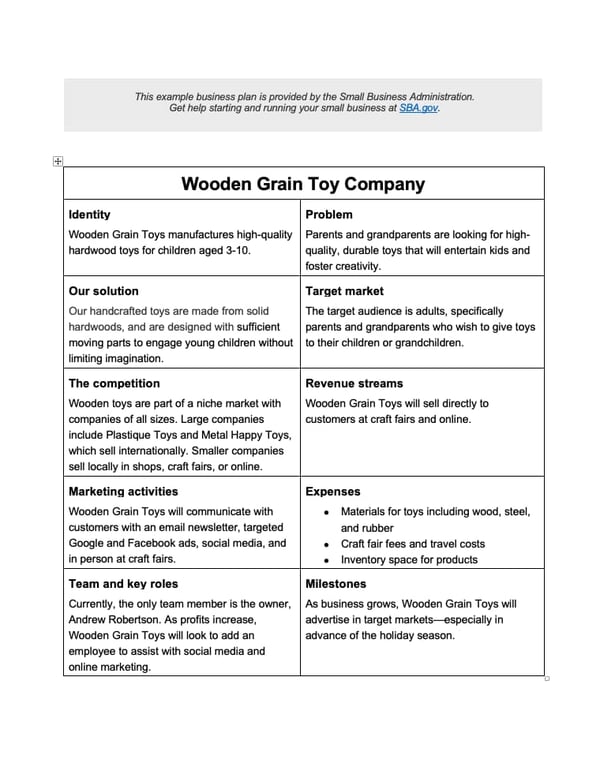
Registry subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesNetlogonParameters
Value Name: ExpectedDialupDelay
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Data Value is in seconds (default= 0 )
Data Range is between 0 and 600 seconds (10 minutes)
For more information, see Settings for minimizing periodic WAN traffic.
Method 3
The IP stack tries to verify the IP address using an ARP broadcast. This delays the time that the IP takes to come online. You can set the ArpRetryCount registry entry to one (1), so the wait for uniqueness is shortened. To do this, follow these steps:
Start Registry Editor.
Locate and select the following subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesTcpIpParametersOn the Edit menu, point to New, and then select DWORD Value.
Type ArpRetryCount.
Right-click the
ArpRetryCountregistry entry, and then select Modify.In the Value data box, type 1, and then select OK.
Note
The Data Range is between 0 and 3 (3 is default).
Exit Registry Editor.
Method 4
Reduce the Netlogon negative cache period by changing the NegativeCachePeriod registry entry in the following subkey:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesNetlogonParametersNegativeCachePeriod
After you make this change, the Netlogon service doesn't behave as if the domain controllers are offline for 45 seconds. The event 5719 is still logged. However, the event doesn't cause any other significant problems. This setting allows member to try domain controllers earlier if the process failed previously.
Suggestion: Try to set a low value, such as three seconds. In LAN environments, you can use a value of 0 to turn off the negative cache.
For more information about this setting, see Settings for minimizing periodic WAN traffic.
Method 5
Configure the Kerberos registry setting to a value that is safely beyond the time that is required allow DC connectivity. Use the following settings as guidelines.
Note
This setting applies only to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 or earlier versions of these systems. Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 and later versions use a default value of 0. This value turns off User Datagram Protocol (UDP) functionality for the Kerberos client.
Registry subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetControlLsaKerberosParameters
Value name: MaxPacketSize
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Value Data: 1
Default: (depends on the system version)
For more information, see How to force Kerberos to use TCP instead of UDP in Windows.
Method 6
Disable media sense for TCP/IP. To do this, add the following value to the Tcpip registry subkey:
Registry subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Value Name: DisableDHCPMediaSense
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Value Data: 1
Value Range: Boolean ( 0 =False, 1 =True)
Default: 0 (False)
For more information, see How to disable the Media Sensing feature for TCP/IP in Windows.
Event Id 1112 Software Installation Tool
Method 7
Group Policy has policy settings to control the wait time for startup policy processing:
Corporate LAN or WLAN:
Policy Folder: 'Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesSystemGroup Policy'
Policy Name: 'Specify startup policy processing wait time'External LAN or WLAN:
Policy Folder: 'Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesSystemGroup Policy'
Policy Name: 'Specify workplace connectivity wait time for policy processing'
The time it takes Netlogon to acquire a working IP can be the basis for the setting. For Direct Access scenarios, you can measure the typical delay your user base has until the connection is established.
Method 8
If DisabledComponents registry setting is in place and has an incorrect value of 0xfffffff, either delete the key or change it to the intended value of 0xff.
Event Id 1112 Software Installation Software
Important
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is a mandatory part of Windows Vista and later versions of Windows. We do not recommend that you disable IPv6 or its components. If you do, some Windows components may not function. Additionally, system startup will be delayed for five seconds if IPv6 is disabled incorrectly by setting the DisabledComponents registry setting to a value of 0xfffffff. The correct value is 0xff.
Method 9
The behavior may be caused by a race condition between network initialization, locating a Domain Controller and processing Group Policy. If the network isn't available, a Domain Controller won't be located, and Group Policy processing will fail. Once the operating system has loaded and a network link is negotiated and established, background refresh of Group Policy will succeed.
You can set a registry value to delay the application of Group Policy:
Start Registry Editor.
Locate and select the following subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogonOn the Edit menu, point to New, and then select DWORD Value.
Type GpNetworkStartTimeoutPolicyValue.
Right-click the
GpNetworkStartTimeoutPolicyValueregistry entry, and then select Modify.Under Base, select Decimal.
In the Value data box, type 60, and then select OK.
Exit Registry Editor, and then restart the computer.
If the Group Policy startup script doesn't run, increase the value of the
GpNetworkStartTimeoutPolicyValueregistry entry.
More information
If you can log on to the domain without a problem, you can safely ignore event ID 5719. Because the Netlogon service may start before the network is ready, the computer may be unable to locate the logon domain controller. Therefore, event ID 5719 is logged. However, after the network is ready, the computer will try again to locate the logon domain controller. In this situation, the operation should be successful.
In a Netogon.log, entries that resemble the following may be logged:
DateTime [CRITICAL] <domain>: NlDiscoverDc: Cannot find DC. DateTime [CRITICAL] <domain>: NlSessionSetup: Session setup: cannot pick trusted DC DateTime [MISC] Eventlog: 5719 (1)'<domain>' 0xc000005e ... DateTime [SESSION] WPNG: NlSetStatusClientSession: Set connection status to c000005e ... DateTime [SESSION] DeviceNetBT_Tcpip_{4A47AF53-40D3-4F92-ACDF-9B5E82A50E32}: Transport Added (10.0.64.232) -> Getting a proper IP address takes >15 seconds.
Event Id 1112 Software Installation Manual
Similar errors might be reported by other components that require Domain Controller connectivity to function correctly. For example, the Group Policy may not be applied at system startup. In this case, startup scripts do not run. The Group Policy failures may be related to the failure of Netlogon to locate a domain controller. You can set Group Policy to be more responsive to late network connectivity arrival.
